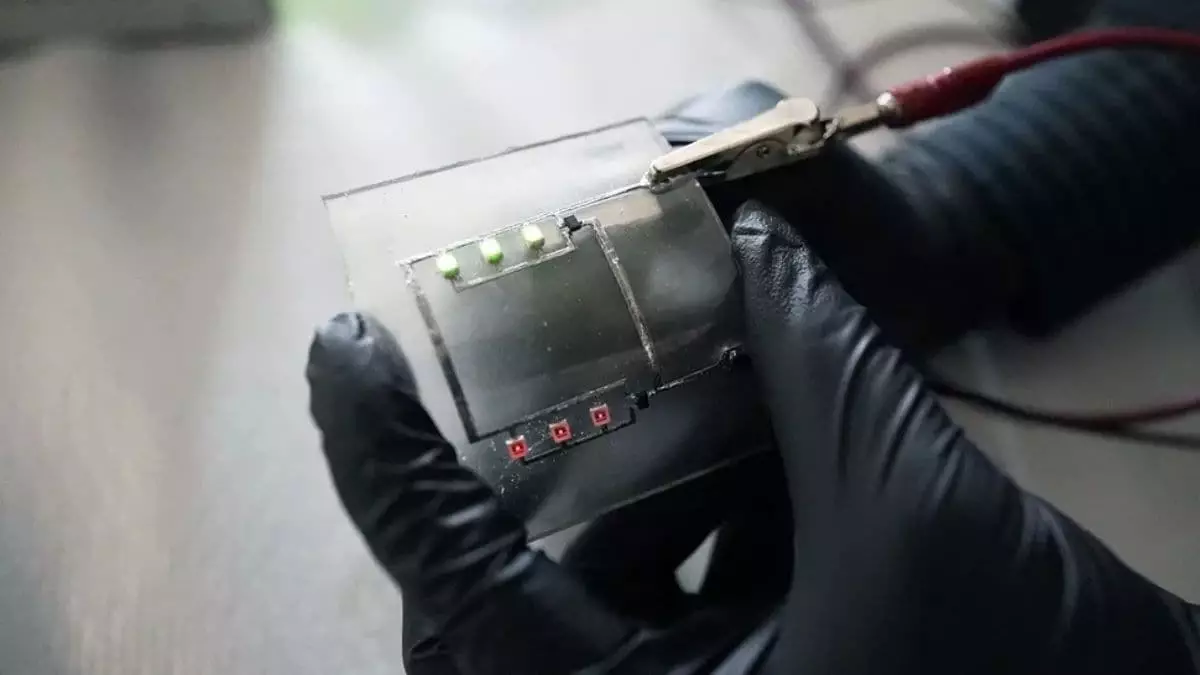
The relentless surge of electronic waste poses a crisis that demands urgent innovation. Traditional circuit boards, while integral to modern life, have remained inherently fragile and non-recyclable, fueling a mounting environmental crisis. The advent of self-healing, heat-reconfigurable circuit boards signals a crucial turning point. This technological breakthrough isn’t merely a step forward; it challenges the very foundation of how consumer electronics are designed, emphasizing resilience and sustainability over disposability. By embedding liquid metal and utilizing flexible polymers like vitrimer, engineers are daring to reimagine a future where electronics are not throwaway commodities but durable, reprocessable assets.
A Bold Leap Toward Sustainability
The core innovation lies in merging vitrimer—an innovative polymer with thermoset strength and reprocessing capability—with liquid metal droplets that serve dual roles as conductors and flexibility enhancers. Unlike conventional boards that crack and end up in landfills, these new materials can be reshaped or repaired simply by applying heat, making electronic devices more resilient to damage and wear. This approach addresses a glaring environmental flaw: current recycling methods are inefficient, and most valuable metals like gold and copper remain trapped within non-recyclable plastics. By enabling easy separation and reusability, this technology advocates for a circular economy in electronics—a concept long championed by environmental advocates and fair-minded policymakers.
Implications Beyond the Laboratory
While the scientific achievements are impressive, the broader implications evoke a nuanced debate about balancing innovation with accessibility and practicality. The potential to retrofit damaged devices extends their lifespan, reducing consumer costs and limiting environmental harm. Yet, the transition from prototype to mass production faces hurdles—costs, regulatory standards, and scalability issues. More critically, relying on novel materials like vitrimer and liquid metal begs questions about long-term stability, safety, and environmental impact of manufacturing and disposal processes. A skeptic might argue that the focus on recycling overlooks deeper issues in consumer culture—namely, the relentless cycle of obsolescence driven by marketing and rapid innovation cycles. For genuine change, technological solutions must be complemented by shifts in consumption habits and policy frameworks that prioritize durability over novelty.
Power Dynamics and Ethical Considerations
The push toward self-healing electronics raises questions about corporate responsibility and ethical priorities. While this technology promises to mitigate environmental degradation, it also empowers large manufacturers to potentially prolong product lifecycles, possibly delaying upgrades or fostering behaviors that discourage innovation. Furthermore, the extraction and processing of liquid metals, although minimal in percentage, still involve environmental and geopolitical concerns that cannot be ignored. Ethical stewardship should demand transparency and equitable access—ensuring such innovations do not become exclusive luxuries for wealthier consumers but serve broader societal needs. Ultimately, true progress hinges on holding stakeholders accountable, integrating environmental justice into technological development, and fostering a culture of sustainability that extends beyond laboratory labs into policy and everyday life.

Leave a Reply