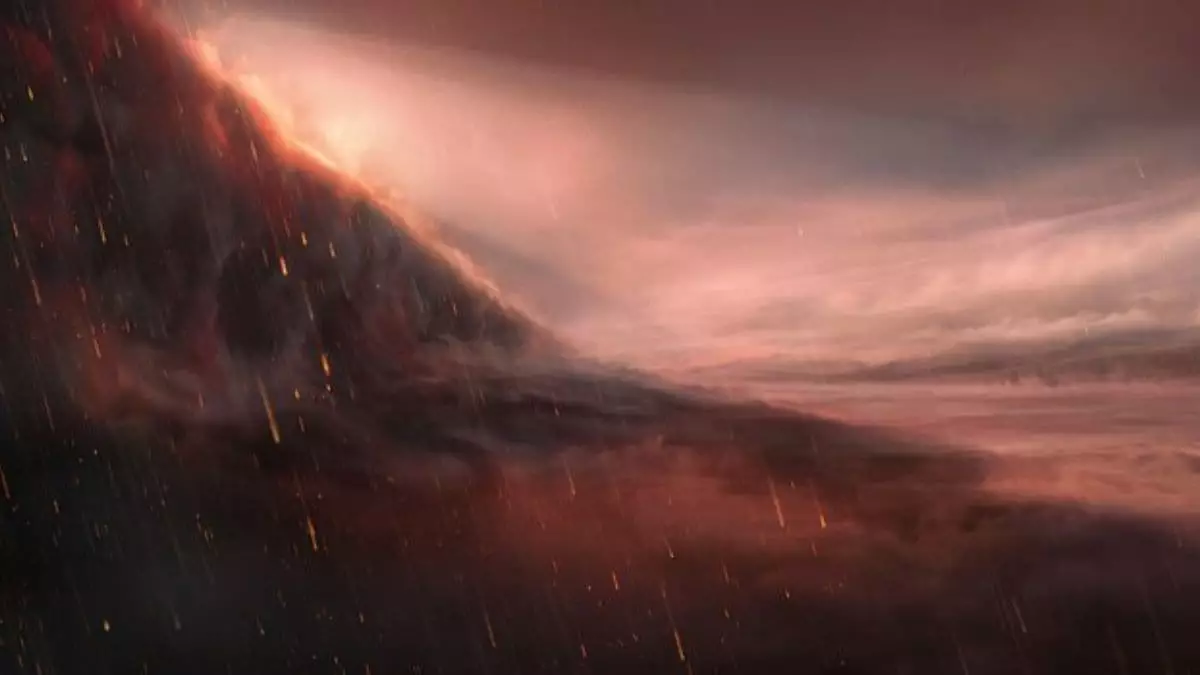
In the vast and expansive universe, the discovery of exoplanets is a testament to humanity’s insatiable curiosity about the cosmos. Among these alien worlds, WASP-121 b stands out due to its extreme atmospheric conditions. This exoplanet, situated approximately 900 light-years from Earth, is characterized by bizarre weather phenomena that challenge our understanding of planetary meteorology. In this article, we will delve into the details of WASP-121 b’s peculiar climate, the scientific advancements that uncovered these features, and the implications for future research into exoplanets.
WASP-121 b belongs to a class known as ultra-hot Jupiters. These giant gas worlds are defined by their extreme temperatures and rapid orbits around their host stars. With a mass that exceeds Jupiter’s by around 20%, WASP-121 b orbits its parent star in just over 30 hours, resulting in a climate that is anything but ordinary. Significantly, the planet is tidally locked, meaning one hemisphere is perpetually bathed in sunlight while the other is shrouded in darkness. This constant exposure to high temperatures causes metals like iron to vaporize in vast quantities, contributing to a dynamic atmosphere filled with metal vapor.
Atmospheric Dynamics and Extreme Weather
Recent studies have illustrated how the interactions between high-speed winds and varying temperatures create intense atmospheric activity on WASP-121 b. Researchers utilizing the Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile’s Atacama Desert have observed remarkable phenomena, such as jet streams that transport vaporized metals across the planet’s atmospheric layers. These powerful currents facilitate the transition of elements from the sweltering dayside, where temperatures soar, to the cooler nightside. There, the vaporized metals condense, resulting in an extraordinary form of precipitation—liquid metal rain.
Dr. Julia Victoria Seidel from the Observatoire de la Côte d’Azur noted that the climate of WASP-121 b defies traditional meteorological models. The planet’s existence expands the boundaries of what scientists believed possible, showcasing a weather system driven not only by thermal dynamics but also by chemical processes involving metals. The detection of titanium in the atmosphere—a finding that surprised researchers—highlights the depth of atmospheric complexity present on this exoplanet.
A major breakthrough in understanding WASP-121 b came with the utilization of the ESPRESSO instrument on the VLT. By combining light gathered from multiple telescopes, scientists were able to discern subtle details in the planet’s atmospheric composition, mapping various layers with unprecedented clarity. This technique allowed for the tracking of lighter elements such as sodium and hydrogen in addition to heavier metals, revealing intricate wind patterns across different altitudes.
Dr. Leonardo A. dos Santos from the Space Telescope Science Institute emphasized that while space telescopes offer a unique vantage point for observing distant worlds, ground-based observatories remain critical for obtaining detailed information. This work represents a significant stride in exoplanetary research, paving the way for future investigations into other distant worlds.
The insights gained from studying WASP-121 b are not merely academic; they hold profound implications for our understanding of atmospheric science beyond our solar system. As we unravel the complexities of exoplanetary atmospheres, we glean information that can inform planetary formation theories and potential habitability assessments. Moreover, the astonishing weather systems observed in WASP-121 b raise questions about the conditions on other exoplanets, potentially leading to the discovery of other worlds with extreme climates.
With advancements in technology and instrumentation, the field of exoplanet research is poised for rapid expansion. Future studies may uncover similar extreme weather patterns on other ultra-hot Jupiters, further refining our knowledge and challenging pre-existing scientific paradigms. As we look to the stars, the experiences of WASP-121 b serve as a reminder of the mysteries waiting to be unveiled in our universe.
The study of WASP-121 b marks a significant milestone in our quest to comprehend exoplanetary atmospheres. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of what we know about these distant worlds, the planet’s metal rain and fierce winds redefine our understanding of what conditions can exist beyond Earth. This unparalleled insight into alien atmospheric dynamics not only enriches our scientific knowledge but also fuels the excitement of discovery in the broader exploration of the cosmos. With every revelation, we edge closer to unveiling the secrets of the universe.

Leave a Reply