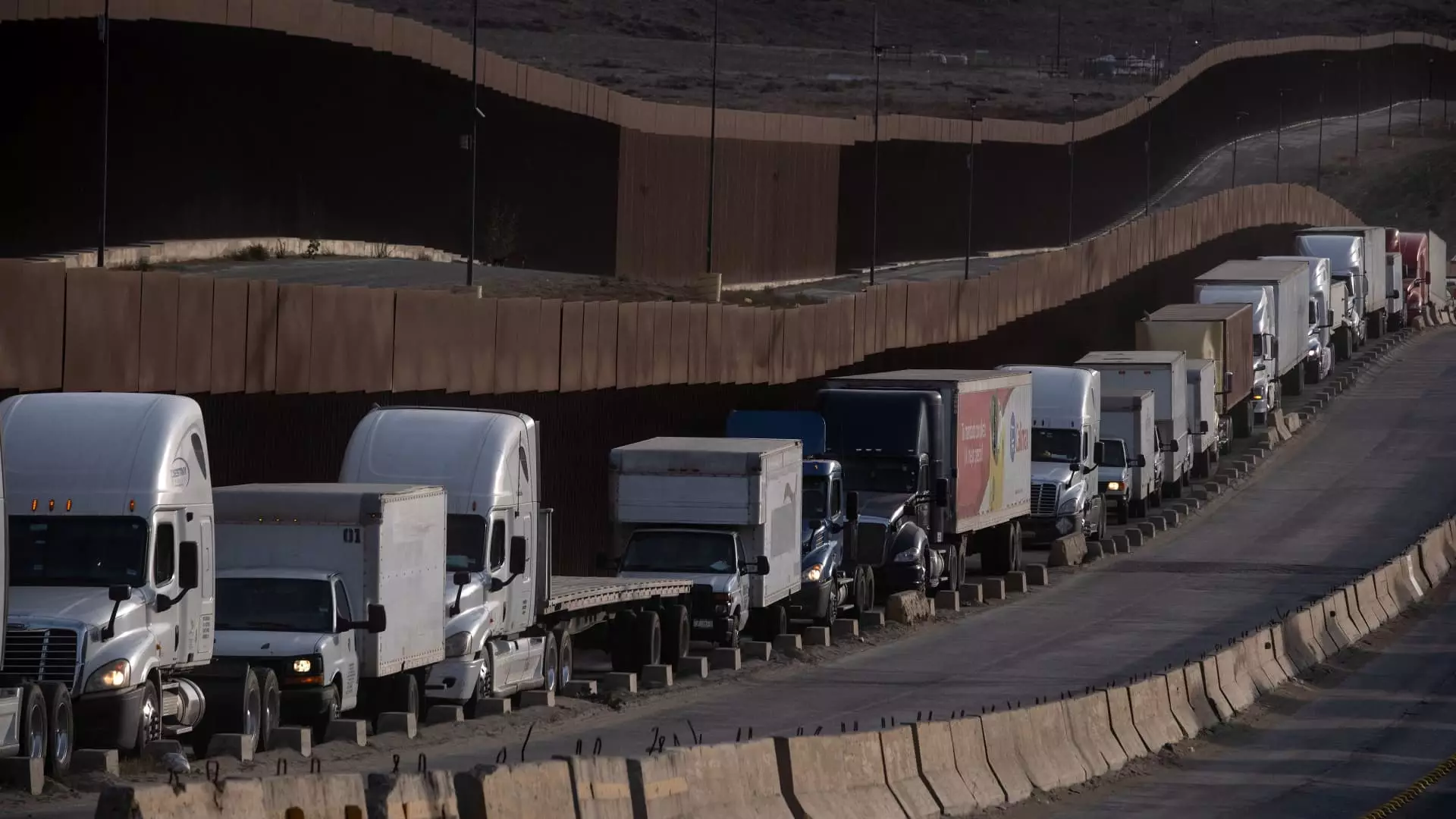
The introduction of tariffs by President Donald Trump represents a significant shift in U.S. trade policy, most notably affecting relationships with major partners such as Canada, Mexico, and China. The implications of these tariffs extend far beyond mere policy changes; they present daunting challenges for U.S. companies whose business operations are intricately tied to these nations. Analyzing the economic landscape, it becomes clear that these tariffs will have a multifaceted impact on growth, inflation, and various sectors, from automotive to retail.
The economic projections surrounding Trump’s proposed tariffs paint a worrying picture. Financial institutions such as Goldman Sachs have forecasted detrimental outcomes, estimating a 0.4% impact on U.S. gross domestic product (GDP) and a considerable 0.7% increase in core inflation if the tariffs on Canada and Mexico are implemented. Dissecting these forecasts reveals a deeper concern: how these cost increases threaten the stability of consumer prices and overall economic growth. The potential inflationary pressures resulting from tariffs could stifle consumer purchasing power, particularly impacting lower-income households.
For businesses reliant on imports and manufacturing from Canada and Mexico, the upcoming tariffs pose a significant threat. Companies like Boot Barn, known for Western clothing, find themselves in a precarious position. With a considerable portion of their production sourced from both Mexico and China, rising tariffs will directly squeeze their profit margins, compelling them to reconsider their supply chain strategies. Analysts, such as Christopher Nardone from Bank of America, highlight how integrated supply chains could face disruptions, prompting companies to either absorb costs or pass them on to consumers.
Moreover, the automotive sector will likely face the most pronounced challenges due to its vast dependence on these regions for production. Major U.S. automakers like Ford and General Motors, who have factories spread across North America, will be forced to navigate the adverse effects of these levies. Financial analysts have pointed out that a significant percentage of production for these automakers occurs in Mexico and Canada, linking their operational success to the stability of these trading relationships. As Austan Goolsbee, president of the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, remarked, there is substantial apprehension among auto executives regarding the implications of tariffs on their pricing structures and overall profitability.
Diving deeper into specific sectors, the challenges become increasingly vivid. The U.S. retail industry, particularly fashion, is poised to experience heightened risks as tariffs may inflate costs and disrupt supply chains. The ripple effects would likely discourage consumer spending, which is crucial to economic recovery. As tariffs raise costs, retailers may resort to price hikes, subsequently impacting sales volume and overall profitability.
The alcoholic beverage sector illustrates another area where tariffs could have severe repercussions. A staggering 83% of U.S. beer imports stem from Mexico, while nearly half of all spirits consumed are also sourced from there. Companies like Constellation Brands, known for premium Mexican imports, stand to suffer significantly. Analysts indicate that manufacturers of beer and spirits may experience margin compression due to tariffs, making cost management all the more crucial as they look to sustain profitability.
Nadine Sarwat of Bernstein noted that Constellation’s revenue heavily relies on its Mexican brand licenses, highlighting the increased vulnerability of firms operating in the import-heavy alcohol market. The potential for soaring inflation, further compounded by tariffs, could carve away at the disposable income of consumers, putting additional pressure on businesses that are already navigating these turbulent waters.
The proposed tariffs on vital trading partners pose substantial risks to various sectors of the U.S. economy. Companies dependent on intricate supply chains are facing tough choices, balancing increased costs against competitive pricing. The automotive and retail industries are particularly at risk, with U.S. manufacturers potentially facing steep price hikes and diminished profit margins. Concurrently, the burden of inflation may place undue stress on consumers, particularly those on the lower economic rungs. As the situation evolves, industries must adapt to these new realities, highlighting the critical importance of strategic planning in a tumultuous economic environment. The knock-on effects of these tariffs will likely resonate throughout the economy, prompting discussions on the sustainability of current trade practices and the enduring impact of protectionist policies.

Leave a Reply